THE FIGO FERTILITY TOOL 7:
HOW TO PREVENT INFERTILITY
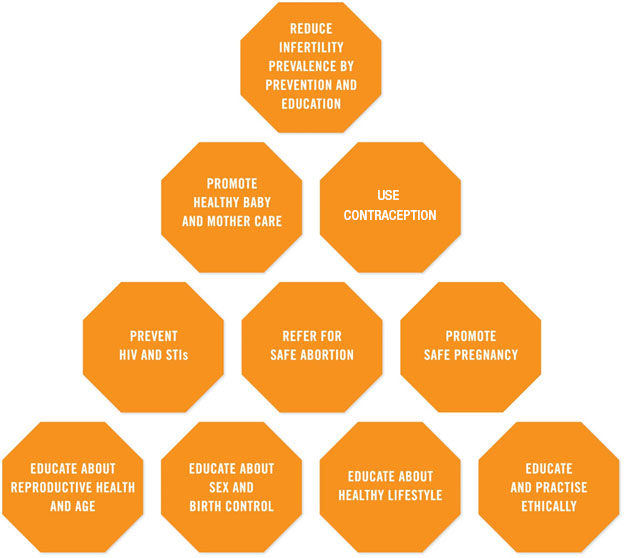
BASIC TOOL 7:
HOW TO PREVENT INFERTILITY
- Educate about reproductive health and age: Everyone needs education about fertility and infertility and the reduction of female fertility with increasing age.
- Educate about sex and birth control: Education about sexual physiology, sex practices, how pregnancy occurs and methods of birth control are important at an early age. With knowledge, women can be empowered to increase their chances of preventing pregnancy that is at too young an age and/or is unwanted.
- Educate about healthy lifestyle: Lifestyle factors such as smoking, under-nutrition, chronic high stress and obesity can substantially reduce fertility. Every educational approach to promote healthy living should clearly address the effect of lifestyle factors on fertility.
- Educate and practise ethically: A critical and essential aspect of providing healthcare is to know how to practice ethically and to practise ethically, especially because individuals, families, society and the healthcare system may have different perspectives about reproduction.
- Prevent HIV and STIs: HIV and other sexually transmitted infections are common, preventable causes of infertility. Professionals and other providers in fertility/infertility programmes should identify and liaise with other professionals, providers and organizations that are involved in HIV and STI education and prevention to coordinate activities that help prevent the transmission of HIV and STIs.
- Refer for safe abortion: Unsafe abortion can cause future infertility. Providers in fertility/infertility programmes should identify and liaise with other providers and organizations that provide safe abortion, to coordinate activities that help all women receive safe abortion services when needed.
- Promote safe pregnancy: Every wanted, healthy baby born to a healthy mother consolidates a family and reduces unmet fertility desires. Professionals and other providers in fertility/infertility programmes should identify and collaborate with other professionals, providers and organizations that promote safe pregnancy.
- Promote healthy baby and mother care: Good neonatal care and healthy motherhood are cornerstones of reproductive health. They optimize current fertility and reduce the risk of future infertility and childlessness. Professionals and other providers in fertility/infertility programmes should identify, support and collaborate with other professionals, providers, organisations and social services that enable and enhance neonatal care and healthy motherhood.
- Use contraception: Preventing unplanned pregnancies protects future fertility. It avoids the risk associated with any pregnancy and the risk of unsafe abortion. Barrier contraceptive methods protect against HIV infection and STIs. Education programmes and social care systems should, from a young age, offer easy and accessible information on the many benefits of preventing, planning (and spacing) pregnancies. Education that enables people to increase the chances of pregnancy when so desired and to prevent pregnancy when so desired should be included in health and education programmes. Safe contraceptive methods should be available to all sexually active women and men.
- Reduce infertility prevalence by prevention and education: Some causes of infertility can be prevented. General education and healthcare prevention strategies can substantially reduce the prevalence and burden of infertility which affects approximately 80 million women and an equivalent number of men worldwide.
